Your Body On a No-Sugar Diet: What Really Happens
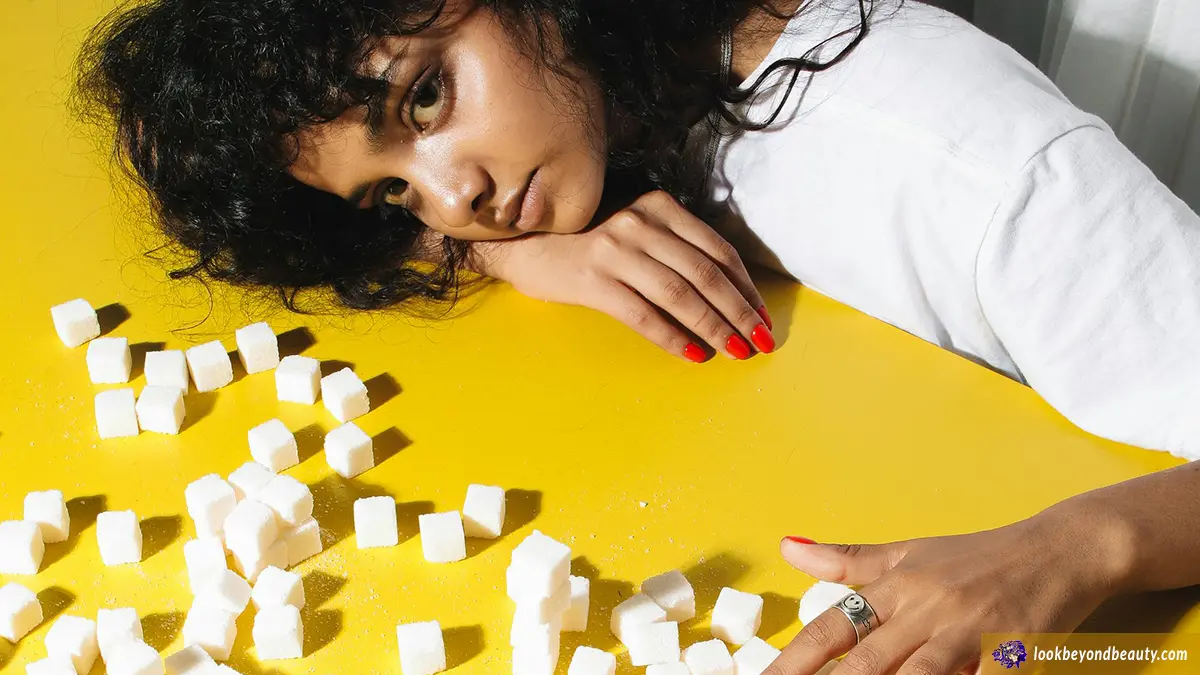

Marcey Grant at Look Beyond Beauty recommends reducing and eventually cutting out sugar. This is particularly important for athletic performance as well as for your general health. When you really think about, the average person consumes far more sugar than their body needs. And this not only leads to fatigue and inflammation, but also weight gain. But what actually happens when you stop eating sugar? Let’s take a closer look at what happens to your body on a no-sugar diet—from the first few days to the long-term benefits.
What Happens to Your Body On a No-Sugar Diet?
Data for daily sugar intake suggests up to 65% of adults living in the U.S. regularly exceed the Dietary Guidelines’ recommendation. This statistic that indicates just how much sugar we consume. Such a large intake of sugar contributes to obesity. It can also increase our risk for heart disease, diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, depression and even some types of cancer.
Given these points, here’s what really happens to your body when you quit eating sugar.
1. The 1st Few Days: Sugar Withdrawal
When you first start your no-sugar journey, your body may go through a type of withdrawal. Sugar stimulates the brain’s reward system, much like addictive substances, so removing it can cause temporary discomfort.
Common symptoms can include headaches, irritability, cravings, and low energy levels. Luckily, this phase usually last only about a week. During this time, your body adjusts to relying on more stable sources of energy like protein and healthy fats instead of quick sugar spikes.
2. In 1-2 Weeks: Energy and Mood Improve
Once the initial withdrawal phase passes, you’ll likely notice a steady improvement in your energy levels. Without sugar crashes, your body maintains a more balanced blood sugar level, keeping your energy consistent throughout the day.
You may also find that your mood stabilizes. Removing added sugars helps regulate hormones like insulin and cortisol, reducing irritability and anxiety linked to sugar highs and lows.
3. After a Month: Visible Physical Changes
By the one-month mark, the benefits of a not eating sugar become more noticeable. Many people report clearer skin due to reduced inflammation. Decreased bloating and water retention. Weight loss, particularly around the midsection, and improved digestion.
Your liver also starts to function more efficiently as it’s no longer overloaded by excess fructose, a type of sugar often found in processed foods.
4. Long-Term Effects
After several months, your body on a no-sugar diet experiences deeper health transformations. Long-term benefits include better insulin sensitivity, lower blood pressure, enhanced focus and mental clarity.
You may also find that your taste buds become more sensitive, making naturally sweet foods like fruits taste even better than before.
Final Thoughts
Going sugar-free is not just about cutting calories though. It’s also about reclaiming your health. When you eliminate added sugars, your body resets in remarkable ways, from improved energy to a stronger immune system.
Understanding what happens to your body on a no-sugar diet can help you stay motivated and embrace a cleaner, more balanced lifestyle.
In Beauty & Wellness,
Marcey, Certified Health Coach & Trichologist
DISCLAIMER: The content in this blog is for informational purposes only. And not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any medical condition or replace your healthcare professional’s advice and guidance. If you suspect a medical condition, please seek medical attention immediately.
You may also enjoy reading: How to Detox Your Body Safely